Coronary Artery Disease: What you need to know
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a prevalent cardiovascular condition characterised by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This disease is a leading cause of heart attacks and other cardiac-related complications worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. What are the causes?
CAD typically develops over time due to plaque buildup within the coronary arteries, a process called atherosclerosis. Plaque consists of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. As plaque accumulates, it narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. In some cases, a plaque may rupture, forming a blood clot that can block blood flow completely, resulting in a heart attack.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of CAD can vary widely among individuals. Some common symptoms include:
Chest Pain (Angina):
This is the most common symptom of CAD. It often feels like pressure, tightness, or discomfort in the chest. It may also manifest as pain or discomfort in the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back.
Shortness of Breath:
Individuals with CAD may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion or emotional stress.
Fatigue:
CAD can cause persistent fatigue or weakness, even with minimal physical activity.
Heart Attack:
In severe cases, CAD can lead to a heart attack, characterised by sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and lightheadedness. A heart attack requires immediate medical attention.
What are the Risk Factors?
Several factors increase the risk of developing CAD, including:
High Blood Pressure:
Hypertension strains the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of CAD.
High Cholesterol:
Elevated LDL cholesterol ("bad" cholesterol) levels can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
Smoking:
Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage the blood vessels and accelerate the progression of CAD.
Diabetes:
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing CAD due to elevated blood sugar levels that damage blood vessels.
Obesity:
Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart and increases the likelihood of developing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Management Strategies:
Once diagnosed with CAD, several management strategies can help control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall heart health.
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Healthy Diet:
Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium while rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage CAD.
Regular Exercise:
Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, helps improve cardiovascular fitness, control weight, and lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Smoking Cessation:
Quitting smoking is crucial for reducing the risk of CAD progression and improving overall heart health.
Stress Management:
Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and improve heart health.
2. Medications:
Cholesterol-lowering Medications:
Statins and other cholesterol-lowering drugs can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
Blood Pressure Medications:
Antihypertensive medications may be prescribed to control high blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart and arteries.
Antiplatelet Therapy:
Drugs such as aspirin or clopidogrel may be prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
Beta-blockers:
These medications help reduce heart rate and blood pressure, relieve symptoms and improve heart function in individuals with CAD.
3. Medical Procedures:
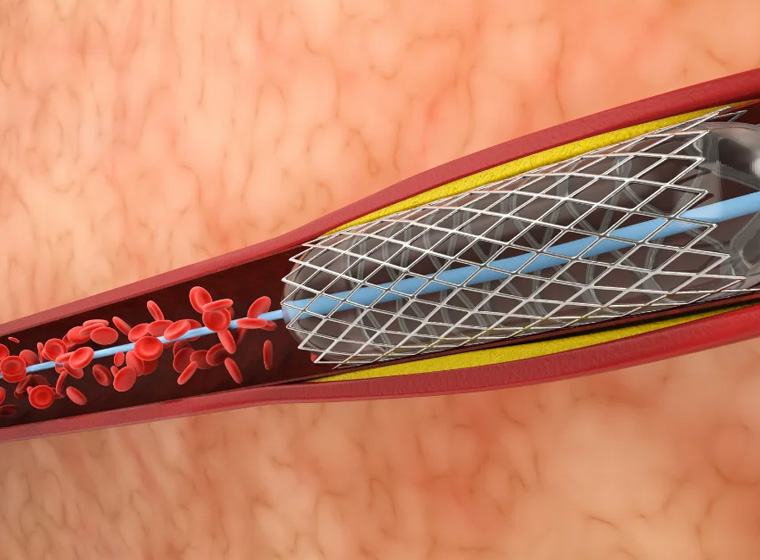
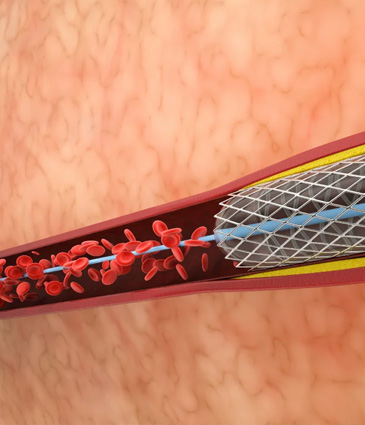
Angioplasty and Stenting:
During angioplasty, a catheter with a balloon at its tip is used to widen narrowed coronary arteries. A stent, a small mesh tube, may be placed to help keep the artery open.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG):
In severe cases of CAD, where multiple coronary arteries are blocked, CABG may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves rerouting blood flow around the blocked arteries using blood vessels from other body parts.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a significant health concern worldwide, contributing to numerous heart-related complications and fatalities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies associated with CAD is essential for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and following medical advice, individuals can reduce the burden of CAD and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Regular medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments are crucial for managing CAD and minimising the risk of complications such as heart attacks and heart failure.