Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Transforming IVF for Better
PRP therapy, also known as intraovarian PRP therapy, has revolutionized the way we approach fertility treatments, offering new hope to couples struggling to conceive. In this article, we will delve into the world of PRP therapy in IVF and explore its role in enhancing fertility.
PRP and its Role in Fertility Treatments
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) has shown promise in addressing ovulatory dysfunction, a significant factor in female infertility. By injecting PRP directly into the ovaries, the rich concentration of growth factors and cytokines may stimulate follicular development. This stimulation can potentially improve egg quality and increase the likelihood of successful conception. Research in this area is ongoing, but early findings suggest that PRP may offer a novel and effective approach to enhance fertility outcomes in women with ovulatory challenges.
A crucial factor in the success of fertility treatments is the receptivity of the endometrial lining. PRP is being explored as a tool to improve endometrial receptivity, creating a more favorable environment for embryo implantation. The application of PRP to the endometrium aims to enhance blood flow and stimulate tissue regeneration, potentially increasing the chances of successful embryo implantation.
The Procedure and Process of PRP Therapy in IVF
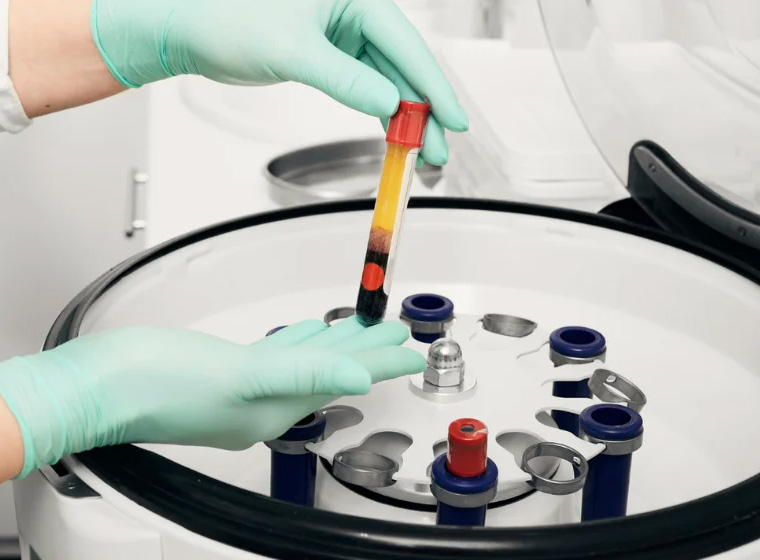
Blood Collection and PRP Isolation:
The first step in PRP therapy for In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) involves the collection of a small blood sample from the patient. Typically drawn from the arm, this blood sample is then subjected to a specialized centrifugation process. Centrifugation separates the platelet-rich plasma (PRP) from other blood components based on density, resulting in a concentrated PRP solution that is rich in growth factors and bioactive proteins.
PRP Injection in IVF:
- Once the PRP is isolated, it is prepared for injection. In the context of IVF, PRP is strategically injected into specific reproductive tissues.
- For female patients, this may involve targeted injections into the ovaries or endometrial lining, depending on the fertility challenges being addressed.
- In male patients, PRP injections can be administered to the reproductive organs to enhance sperm production and function.
The rationale behind PRP therapy in IVF is to harness the regenerative and healing properties of platelets to optimize the reproductive environment. By improving ovarian function, egg quality, and endometrial receptivity, PRP aims to enhance the overall success rates of IVF procedures.
PRP and its Impact on Fertility
PRP therapy exhibits promising outcomes in elevating fertility levels through its ability to enhance the holistic well-being of the reproductive system. The rich reservoir of growth factors and cytokines within PRP serves as a catalyst, stimulating the development of robust and healthy eggs.
Concurrently, it facilitates the creation of a more receptive uterine lining, thereby amplifying the likelihood of successful embryo implantation.
Moreover, PRP therapy goes beyond surface improvements by effectively enhancing ovarian function and addressing hormonal imbalances. This comprehensive approach tackles underlying issues associated with infertility, showcasing the versatility of PRP in promoting reproductive health.
The cumulative effect of these mechanisms positions PRP therapy as a multifaceted intervention, offering a potential avenue for individuals seeking to optimize their fertility and overcome impediments to conception.
Potential Benefits of PRP in IVF
Improved Endometrial Receptivity:
PRP is thought to promote tissue healing and regeneration. It may enhance the quality and receptivity of the endometrial lining, providing a more favorable environment for embryo implantation.
Enhanced Ovarian Function:
Some studies propose that PRP may stimulate ovarian function and follicular development. This could be beneficial for women with diminished ovarian reserve or poor response to conventional ovarian stimulation protocols. The latest NIH study demonstrated that PRP treatment resulted in a higher Antral Follicle Count (AFC), increased serum Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH), and lower serum Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), suggesting stimulation of ovarian function and improved follicular development.
Reduced Inflammation:
PRP has anti-inflammatory properties, and by reducing inflammation in the reproductive organs, it may create a more favorable environment for successful embryo implantation.
Increased Vascularization:
PRP may stimulate angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), which could improve blood flow to the uterus and ovaries, potentially benefiting reproductive outcomes.
Support for Implantation and Early Pregnancy:
The growth factors in PRP might play a role in supporting early embryonic development and implantation, leading to improved pregnancy rates.
Candidates for PRP Therapy in IVF
Recurrent Implantation Failure (RIF):
Women who have experienced multiple failed IVF cycles despite good-quality embryos may be considered for PRP therapy to enhance endometrial receptivity.
Diminished Ovarian Reserve (DOR):
Women with diminished ovarian reserve, characterized by a low ovarian egg quantity, may also be potential candidates for PRP to stimulate ovarian function and improve follicular development. The NIH study demonstrated that PRP treatment resulted in a higher Antral Follicle Count (AFC), increased serum Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH), and lower serum Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), suggesting stimulation of ovarian function and improved follicular development.
Thin Endometrium:
PRP may be considered for women with a thin endometrial lining, as it is believed to promote the growth and thickening of the endometrium.
Advanced Maternal Age:
Older women who may experience age-related declines in reproductive function might be considered for PRP to improve ovarian function and endometrial receptivity. The NIH study also indicated improvements in ovarian reserve parameters, a pregnancy rate of 20.5%, and a sustained implantation/live birth rate of 12.9% after PRP treatment in women with poor ovarian response.
How PRP Therapy is Administered in IVF Procedures
PRP therapy is administered during the IVF procedure itself, complementing the existing protocols. After the eggs are retrieved and fertilized in the laboratory, the PRP solution is carefully injected into the ovaries or uterus. This targeted approach ensures that the growth factors and cytokines in PRP directly influence the reproductive organs, maximizing their regenerative effects.
Conclusion
PRP therapy is transforming fertility treatments, bringing fresh hope to couples trying to conceive. By leveraging the regenerative properties of platelets, it boosts IVF success rates and enhances reproductive health naturally. This minimally invasive approach stands out, addressing infertility at its roots and promoting the body's natural healing.
Contact "IMA" for PRP Fertility Treatment
If you are seeking a solution to infertility and are interested in exploring the benefits of PRP therapy in IVF, contact Istanbul Med Assist (IMA) today. Our team of experienced fertility specialists and state-of-the-art facilities ensure personalized and comprehensive care throughout your journey towards parenthood.
Take the first step towards realizing your dream of starting a family by reaching out to IMA and discovering the power of PRP therapy in IVF.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Price Turkey